Új hozzászólás Aktív témák
-
BCLK ügyében ennyit találtam:
https://en.wikichip.org/wiki/intel/microarchitectures/skylake_(server)DMI/PEG are now on a discrete clock domain with BCLK sitting on its own domain with full-range granularity (1 MHz intervals)
Elvileg nincs összekötve a pcie-velViszont ami lényeges bár a szervernél nem csak a cliensnél említik:
https://en.wikichip.org/wiki/intel/microarchitectures/skylake_(client)
The BCLK in Skylake has undergone dramatic architectural changes. Considerable effort was dedicated to separating the DMI and PEG (PCIe & Graphics), allowing DMI/PEG to run at their nominal ~100 MHz clock in their own isolated clock domain. This allows BCLK to run at very high speeds (200 MHz+ with upward of 400 MHz+ in LN2). Additionally, while the BCLK is typically supplied by the chipset internal clock generator, it's also possible to supply the clock externally; i.e., motherboard ODMs can potentially take advantage of this and offer their own discrete BCLK control.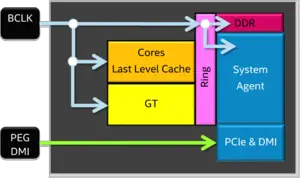
Overclocking may involve changing the BCLK frequency. Because a large number of components operate their own clock domains as a multiple of the BCLK, an increase of 10% to the BCLK frequency will result in an increase of 10% to all other components. On Skylake, the PCIe & DMI sit on their own dedicated reference clock.Magyarán a bclk-t vagy a chipset állítja elő vagy a lap saját PLL-je. Értelem szerűen amely lapon állítható biosból az saját pll-t használ. Chipset álltal előállított nem tudom hogyan képzeljem el és hogy állítható-e egyáltalán valami regiszterből.
Új hozzászólás Aktív témák
- Rugalmas OLED panelre válthat a Samsung Galaxy A57
- czundermák: Shikoku Henro #0: Mégis mi ez?
- One otthoni szolgáltatások (TV, internet, telefon)
- Milyen okostelefont vegyek?
- Samsung Galaxy A54 - türelemjáték
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5080 / 5090 (GB203 / 202)
- sziku69: Fűzzük össze a szavakat :)
- Luck Dragon: Asszociációs játék. :)
- Vicces képek
- CES 2026: jön az AMD CES előadása és az NVIDIA GeForce ON
- További aktív témák...
- BESZÁMÍTÁS! MSI B760M i7 14700K 32GB DDR5 1TB SSD RX 9070 XT 16GB Lian Li Lancool 207 Digital 750W
- Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra - Green - 8GB /256GB - Újszerű állapot!
- Samsung Galaxy A53 5G 128GB, Kártyafüggetlen, 1 Év Garanciával
- HIBÁTLAN iPhone 14 256GB Purple -1 ÉV GARANCIA - Kártyafüggetlen, MS3535
- ÁRGARANCIA!Épített KomPhone i5 14400F 32/64GB RAM RX 9060 XT 16GB GAMER PC termékbeszámítással
Állásajánlatok
Cég: Laptopszaki Kft.
Város: Budapest
Cég: PCMENTOR SZERVIZ KFT.
Város: Budapest


